SPACE WEATHER SCIENCE
FASCINATING SCIENCE - UNLIMITED POTENTIAL
THIS SITE IS UNDER CONSTRUCTION. ALL THE DATA USED HERE NOW ARE ONLY DUMMY AND FOR DEVELOPMENT AND REPRESENTATION PURPOSE ONLY. PLEASE DO NOT USE THIS DATA UNTIL THE SITE IS DECLARED ACTIVE.
CURRENT SPACE WEATHER
This page provides the information of the current and the most recent parameters related to the space weather.
The values are measured by satellites like SDO, ACE, DSCOVR etc. or by the ground based instruments like the magnetometers or the ionosondes.
The relevant tabs gives an organized demarcation of different parameters pertaining to the Sun, the solar wind, the magnetosphere or the ionosphere.
Data from the last one week or last one solar rotation are provided for different parameters.
All the data in one place and with well organized interface provides a very efficient and comprehensive representation of the current space weather.
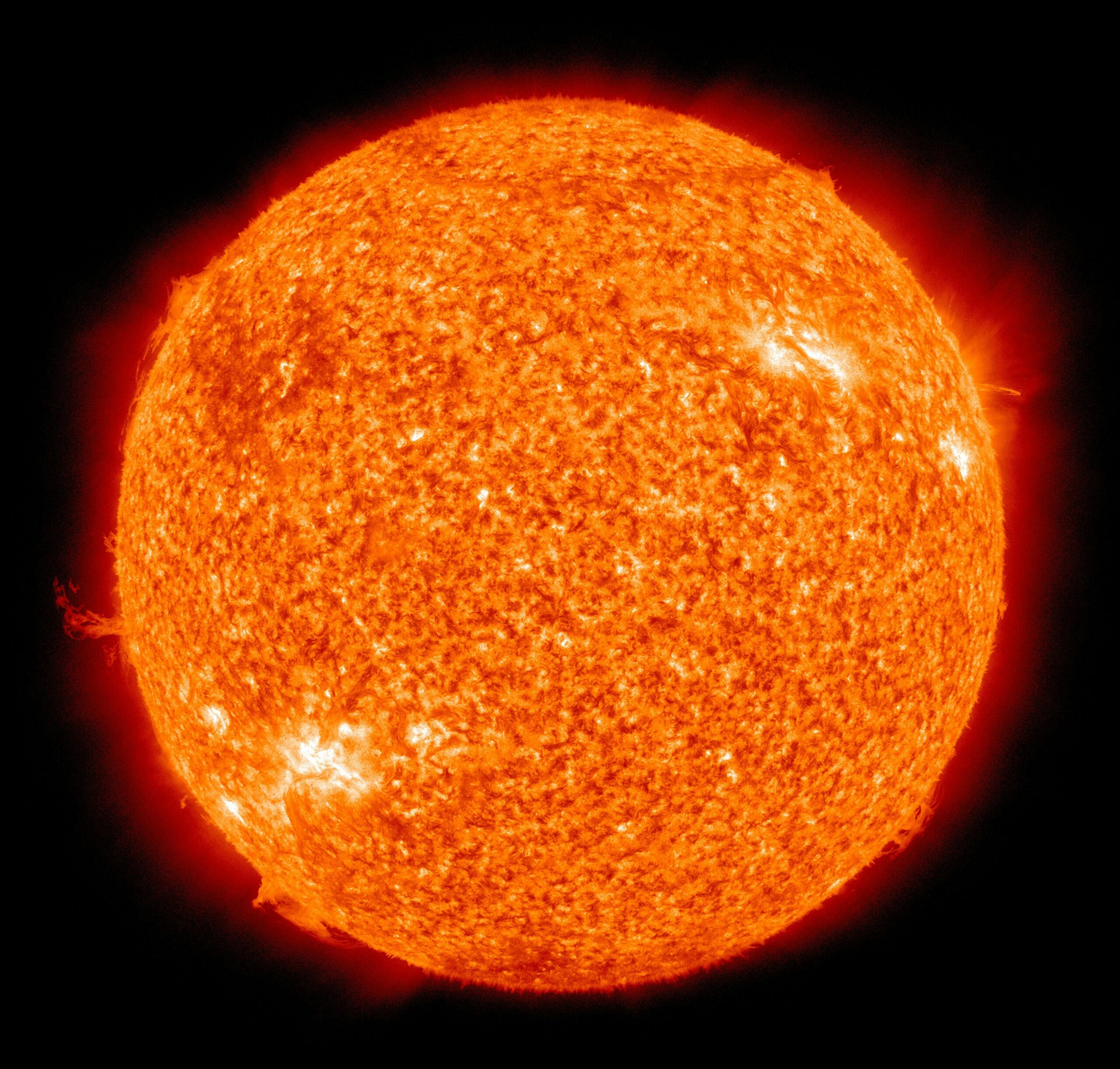
SUN

SOLAR WIND

MAGNETOSPHERE

IONOSPHERE
The Sun is imaged with different filters, allowing lights of different frequencies, to pass and form the image. Different frequencies carry information from different dephts of the solar corona.
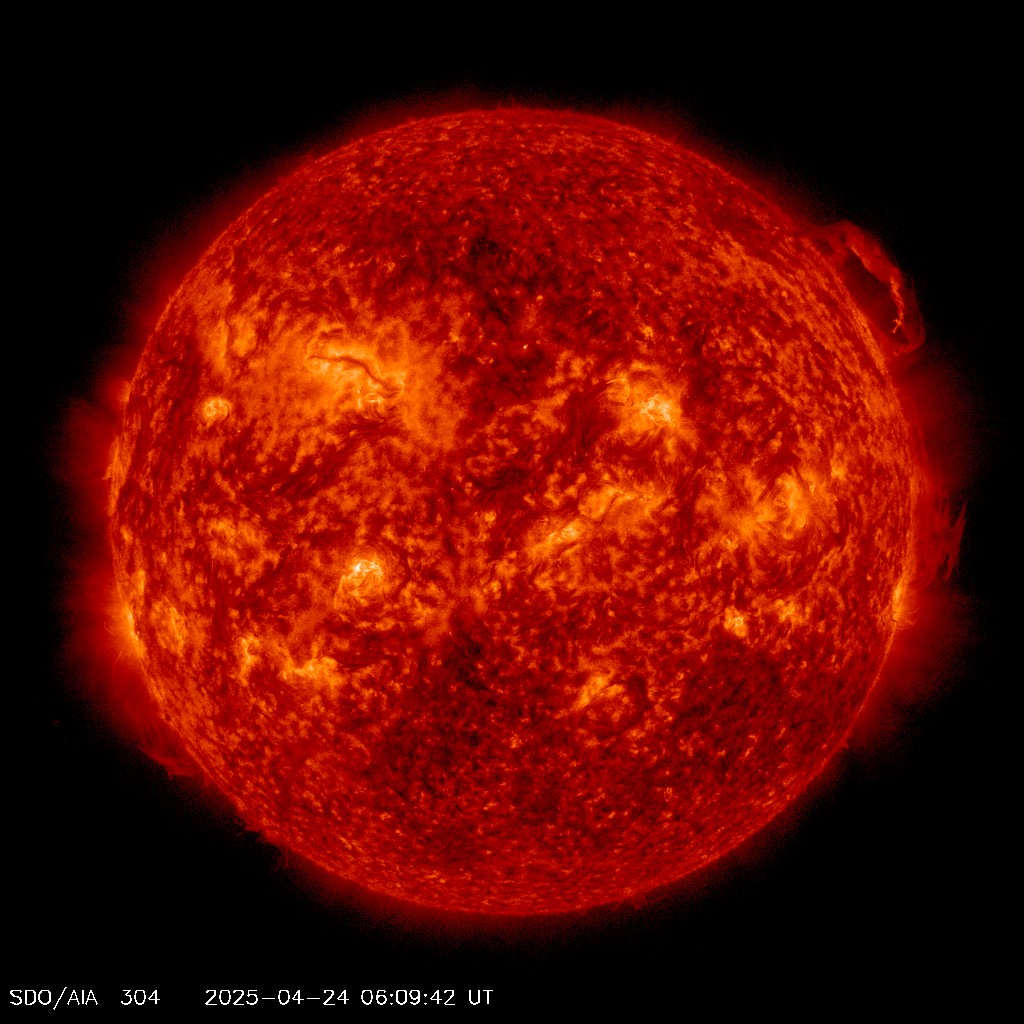
The current image of the Sun at 304 A.
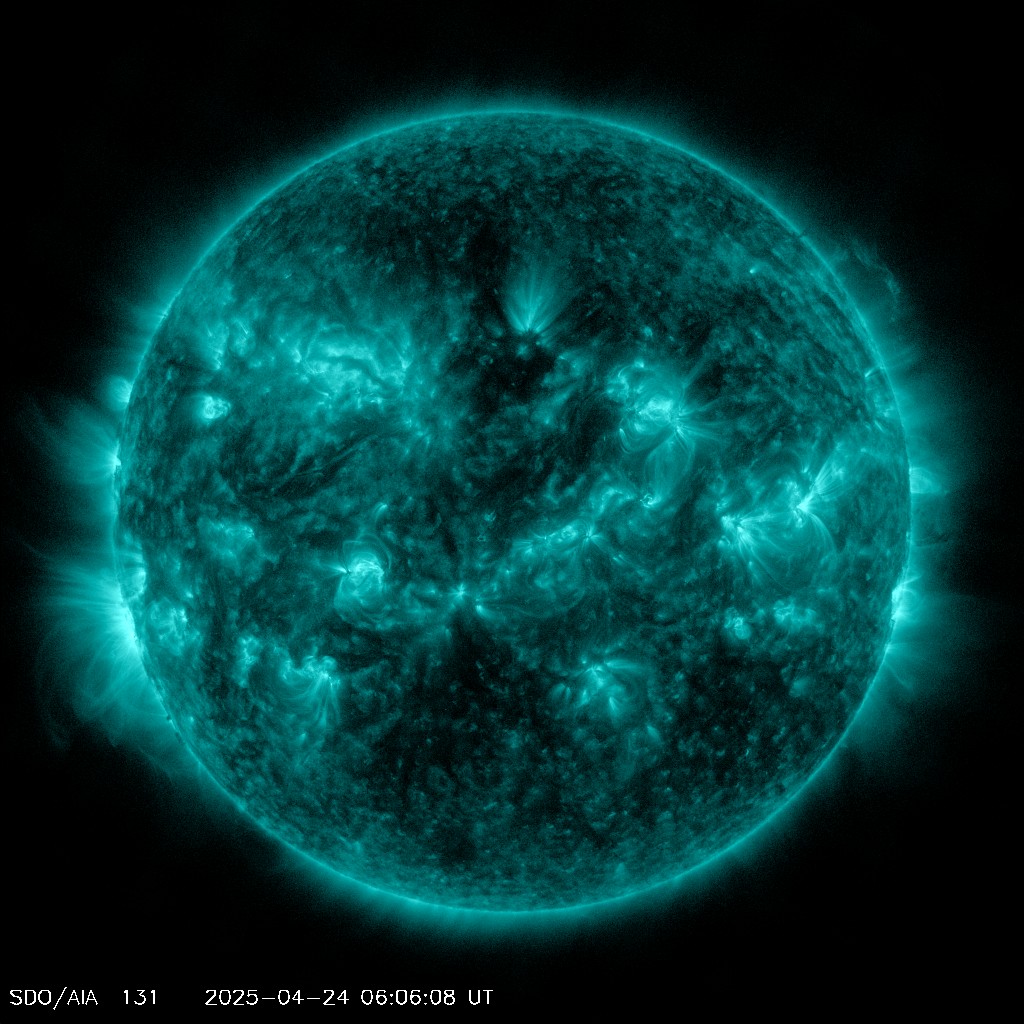
The current image of the Sun at 131 A.
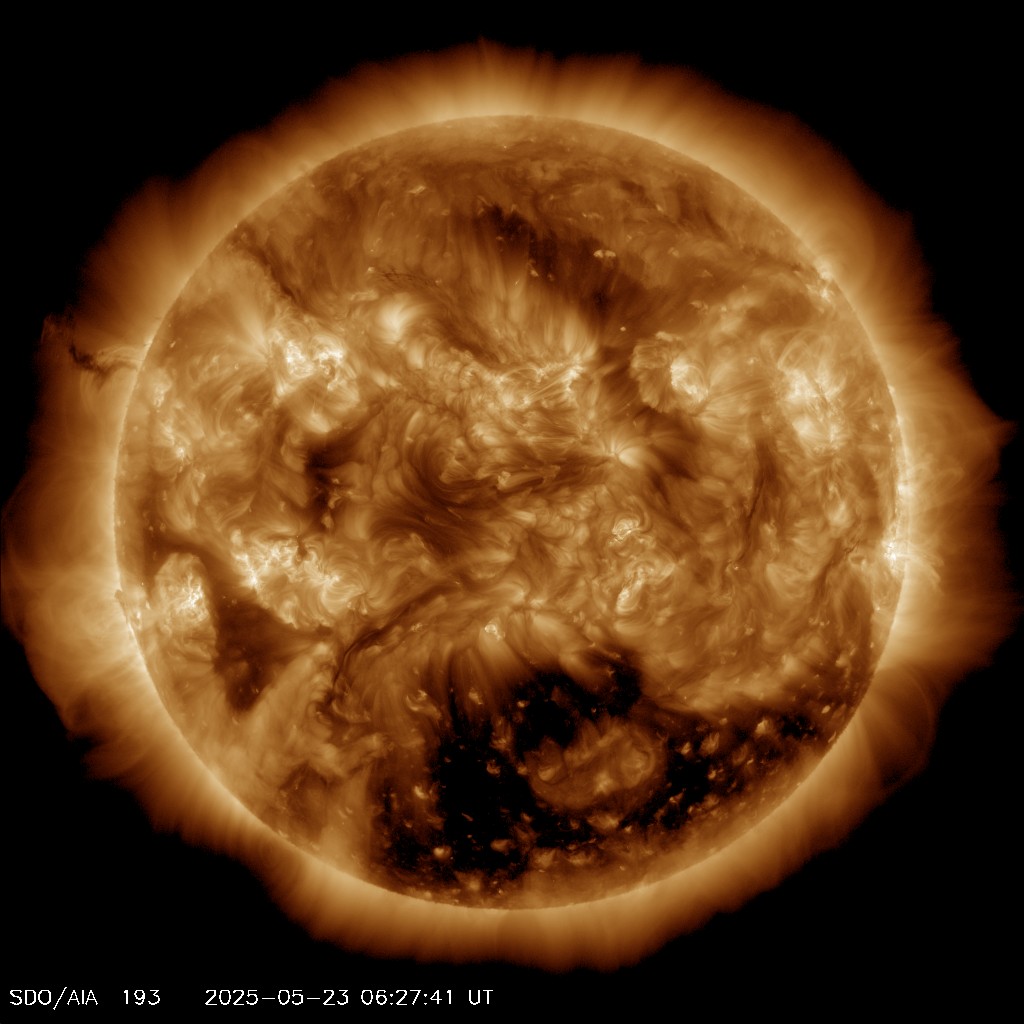
The current image of the Sun at 193 A.
The source of all Space Weather is the Sun and its activities. Therefore the following solar parameters, which act as the drivers for the space weather and immense important for understanding the existing weather and the extent of its potential effects
IMPORTANT PARAMETERS
Bertels Rotation Number: 2613
Start Date:
Current Date:
Solar Activity Cycle No. : 25
Start Year : 2019
End Year : 2030
Stage : 51%
Sunspot Number: 114
Active Region: AC1039
F10.7 : 094
SUNSPOT NUMBER
Sunspots are the relatively cooler dark areas on the Sun's surface
 + new Time())
Sunspot numbers reflects the intensity of the solar magnetic activity
 + new Time())
F10.7
This is the total solar flux at the 10.7 cm wavelength
 + new Time())
10.7cm represents the weighted mean of the all radiations by the Sun
 + new Time())
The following parameters represent the particle or wave emissions. They can directly affect the earth's atmosphere and ionosphere from within a few minutes to few hours interval from the time of their occurrences.r daily and weekly values are availavbe in the plots.
SOLAR PARTICALE FLUX
The amount of energetic particles and radiation emissions from the Sun
 + new Time())
- PFU: Proton Flux Unit;
- 1 PFU =
 + new Time())
SOLAR X-RAY FLUX
The amount of energetic particles and radiation emissions from the Sun
 + new Time())
X-Ray Flux Unit is W/m^2
X-Ray flux > 10^-4 : Class X flare
 + new Time())
X-Ray Flux Unit is W/m^2
X-Ray flux > 10^-4 : Class X flare
CORONAGRAPH AND DOPPLER
Coronagraph provides the image of the Sun's corona (the outer atmosphere of Sun)
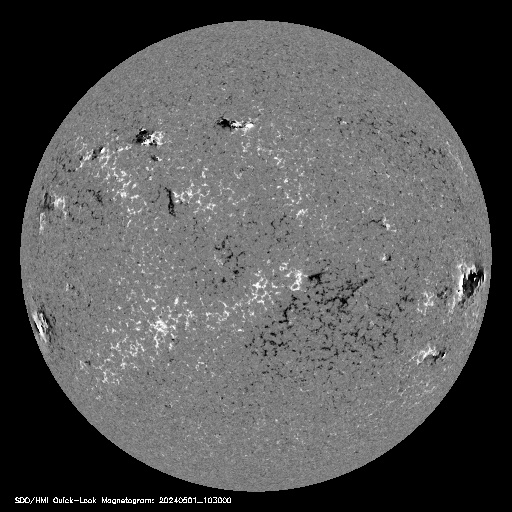
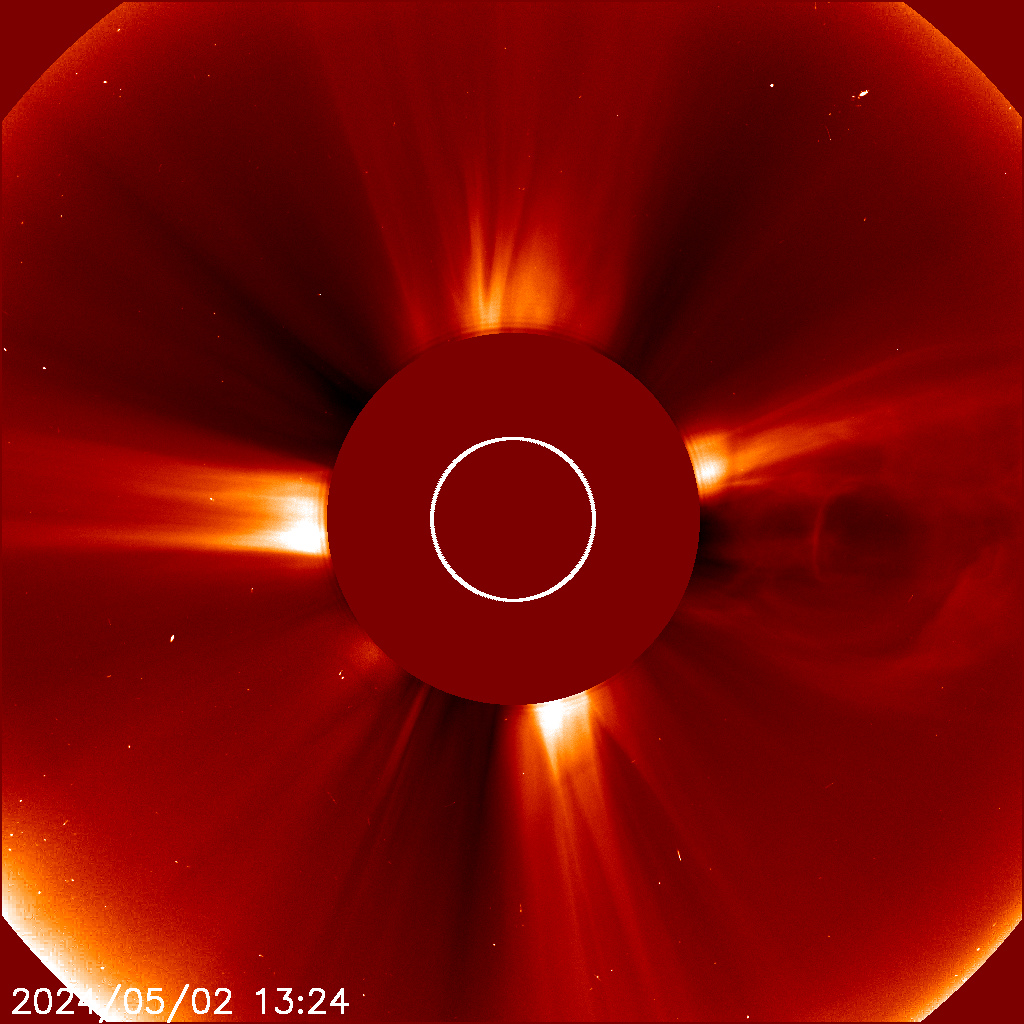

The point of using dummy text for your paragraph is that it has a more-or-less normal distribution of letters. making it look like readable English.
The solar winds are the perennial flow of charged particles (plasma) emitted from the Sun. These hot plasma fills up the interplanetary space and flow downstream towards the edge of the heliosphere. The wind parameters are measured at a location near to the earth, mostly at the Lagrangian point, L1.
SOLAR WIND VELOCITY
The solar wind flows through interplanetary space with velocities of few hundreds of kmps
 + new Time())
 + new Time())
SOLAR WIND DENSITY
Solar wind is mostly constituted by Hydrogen ions with varying density
 + new Time())
 + new Time())
SOLAR WIND TEMPERATURE
Ion temperature of the solar wind particles represents their average kinetic energy
 + new Time())
 + new Time())
The interplanetary magnetic field fills up the interplanetary space. These magnetic fields have their sources at the Sun and is carried into the interplanetary space by the hot plasma of the solar wind which remians frozen with it. These fields are measured with respect to a geocentric reference frame GSE.
IMF Bz
It is the strength and orientation of Bz that determines the disruption in magnetosphere
 + new Time())
 + new Time())
IMF Bx
It is the X component of the IMF when measured in GSE reference.
IMF By
It is the Y component of the IMF when measured in GSE reference.
The derived parameters tells a lot about the behaviour of the Solar Wind. The Parker's angle and clock angle provides the relative orientation of the IMF with respect to the earth and its orbit. The ram pressure reveals the strength of the wind to disrupt the benign magnetospheric nature while the distribution of the fast and slow solar wind let us understand the dominant region of the sun that emits the wind.
PARKER'S AND CLOCK ANGLES
The Parkers angle is the angle made by the solar with the earth's orbit.
RAM PRESSURE
Ram pressure is the thrusht provided by the solar wind on the magnetospheric surface.
 + new Time())
 + new Time())
FAST/SLOW WIND DISTRIBUTION
Slow and fast winds are dominant during high and low activity periods respectively
The point of using dummy text for your paragraph is that it has a more-or-less normal distribution of letters. making it look like readable English.
The magnetosphere acts as a shield that rpotects Earth from the disruptions of the solar wind. However, the magnetospheric features change with the variation of the solar wind emitted from the Sun. Here we present the most salient features of the magnetosphere that are influenced by the impinging solar wind and the associated IMF.
MAGNETOSPHERIC RADIUS
The radial periphery of the magnetosphere measured in Re.
 + new Time())
 + new Time())
POLAR CAP POTENTIAL
The electric potential developed across the polar cap due to magnetospheric convection
 + new Time())
 + new Time())
CLOCK ANGLE
Although clock angle is an IMF parameter, it determines many magnetospheric conditions
 + new Time())
 + new Time())
There are different states of the geomagnetic fields which are determined by various direct and proxy indices. These indices are determined from measurements done on ground or obtained through various models.
Ae
Although Ae is an ionospheric current, it reveals various magnetospheric conditions
 + new Time())
 + new Time())
PLASMA SHEET STATE
The point of using dummy text for your paragraph is that it has a more-or-less normal
 + new Time())
 + new Time())
GEOMAGNETIC FIELDS
These are the magnetometers data that represents the North geomagnetic fields
 + new Time())
 + new Time())
The near-surface geomagnetic fields undergo severe perturbation when space weather event affects the magnetosphere and its elements. This inturn alters the behaviour of the ionosphere and results in geomagnetic storm and substorms.
Dst
Dst is the depreciation of northward geomagnetic field from the nominal value
 + new Time())
 + new Time())
Ap
Ap index is the global average of deviations of the midlatitude magnetic field in linear scale
 + new Time())
 + new Time())
Kp
Kp index is the global average of deviations of the midlatitude magnetic field in log scale
 + new Time())
 + new Time())
The point of using dummy text for your paragraph is that it has a more-or-less normal distribution of letters. making it look like readable English.
Important: Plots are derived at spaceweathersci.com from data available at SWPC. These are for educational purpose only and the values may contain errors.
"Courtesy of NASA/SDO and the AIA, EVE, and HMI science teams."